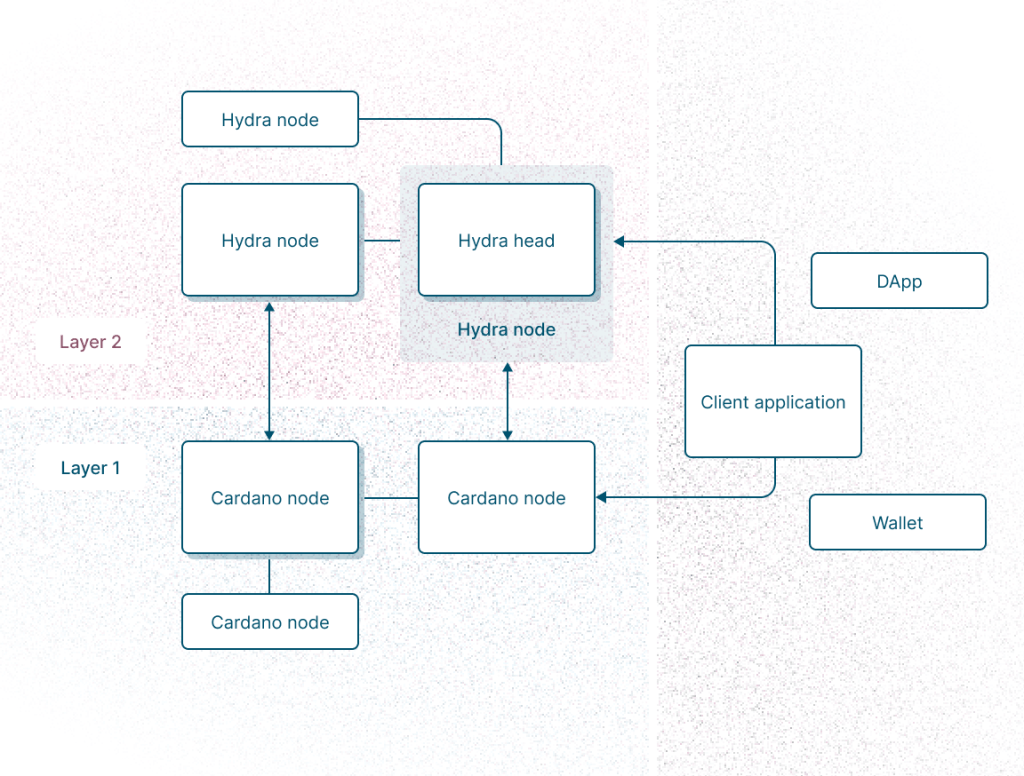
The Hydra Head protocol is a layer 2 scaling solution for Cardano rooted in peer-reviewed research that increases transaction throughput and ensures cost efficiency while maintaining rigorous security.
The paper “The Hydra Head Protocol” introduces a layer 2 scalability solution for the Cardano blockchain, designed to enhance transaction throughput while maintaining security and decentralization. The protocol is based on state channels, allowing multiple parties to transact off-chain efficiently while preserving the blockchain’s security guarantees.
1. Problem: Scalability in Blockchain Networks
Public blockchains, including Cardano, face scalability challenges due to:
- Limited transaction throughput: Blocks have fixed sizes and intervals, restricting the number of transactions per second (TPS).
- High fees and congestion: More users lead to network congestion, raising transaction costs.
- Latency: Transactions need multiple confirmations before finality, slowing down processing.
The Hydra Head protocol aims to solve these issues by enabling off-chain transaction processing while ensuring the same security guarantees as the main blockchain.
2. Hydra Head: A Layer 2 State Channel Solution
A Hydra Head is a state channel that allows a small group of participants to conduct fast and cost-effective transactions off-chain. These transactions only need to be settled on-chain when required.
How Hydra Heads Work
- A group of users locks funds into a Hydra Head via an on-chain smart contract.
- Once the head is open, users can perform instant off-chain transactions with each other.
- When participants wish to close the channel, the final state is submitted back to the main chain.
Key Features of Hydra Heads
✅ Off-chain transaction processing → Near-instant transactions without network congestion.
✅ Trustless and secure → Participants can always revert to the on-chain state, preventing fraud.
✅ Parallel execution → Multiple Hydra Heads can run simultaneously, scaling linearly with the number of users.
3. Security and Finality in Hydra
Hydra ensures that:
- Transactions inside a Hydra Head are cryptographically secure and follow the same rules as on-chain transactions.
- If a dispute arises, participants can enforce the last known valid state on the main blockchain.
- The protocol provides fast settlement (even for complex transactions), reducing latency.
4. Performance and Scalability
- High TPS (Transactions Per Second): Each Hydra Head can process 1,000+ transactions per second, and multiple heads can run in parallel.
- Efficient resource usage: Since transactions happen off-chain, they don’t add load to the Cardano blockchain.
- Cost-effective: Users pay lower fees because most transactions do not need to be recorded on-chain.
5. Use Cases and Applications
Hydra Heads are versatile and can benefit various use cases:
🔹 Micropayments → Faster, cheaper payments for daily transactions.
🔹 DeFi & Smart Contracts → Scalable execution of smart contracts without network congestion.
🔹 Gaming & NFTs → Secure, high-speed transactions for in-game economies and NFT marketplaces.
🔹 IoT & Machine-to-Machine Transactions → Real-time data exchange between connected devices.
One notable partnership utilizing the Hydra Head protocol is between IOG (Input Output Global), the primary development team behind Cardano, and Obsidian Systems, a blockchain development firm.
Objective of the Partnership
The collaboration aims to enhance the adoption and real-world implementation of Hydra Heads, focusing on scaling transaction throughput for financial applications, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and real-time payments.
Use Case: Hydra for Payments & DeFi
- Obsidian Systems explores integrating Hydra Heads into DeFi applications, enabling high-speed, low-cost transactions.
- A key use case is scalable payment processing for merchants, allowing instant settlement without blockchain congestion.
- The partnership investigates DEX improvements, where Hydra Heads can facilitate off-chain order matching while ensuring secure on-chain settlements.
The Hydra Doom experiment
The Hydra Doom experiment was an innovative initiative by the Cardano blockchain to demonstrate the capabilities of its Layer-2 scaling solution, Hydra. By running the classic first-person shooter game Doom within the Hydra framework, Cardano showcased its potential to handle extremely high transaction volumes efficiently.
Hydra Protocol Overview:
Hydra is designed to enhance Cardano’s scalability by creating off-chain environments called “Hydra Heads.” Within these heads, transactions are processed off the main blockchain, allowing for rapid and cost-effective operations. Once the interactions are complete, the final state is settled back on the main chain, ensuring security and decentralization.
Doom Integration:
In this experiment, each action in the Doom game was treated as a transaction within a Hydra Head. This setup enabled the game to run in real-time, with the blockchain validating each frame and player action. The deterministic nature of both Cardano transactions and Doom’s engine ensured consistent game state evolution, preventing cheating and maintaining integrity.
Achievements:
During the Hydra Doom Tournament, Cardano’s network achieved a peak performance of over 1 million transactions per second (TPS), surpassing other blockchain networks. This accomplishment underscores Hydra’s potential to handle high-demand applications beyond gaming, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and payment systems.
Future Prospects:
Following the success of the Doom experiment, Cardano plans to integrate Hydra into real-world applications, including DeFi, payments, and gaming experiences. Collaborations with projects like Anastasia Labs’ Midgard and Sundae Labs’ Gummiworm are underway to implement Hydra’s scalability features into practical use cases.
The Hydra Doom experiment not only highlighted Cardano’s technical advancements but also opened avenues for future applications that require high throughput and low latency, reinforcing Cardano’s position in the evolving blockchain landscape.
For a deeper insight into the development of the Hydra Doom experience, you might find this video informative:
Glacier Drop by Midnight takes a historic step on Cardano by operating on Hydra
The founder of Cardano, Charles Hoskinson, announced on his X account that Midnight’s Glacier Drop event is running on Hydra, one of the network’s most advanced scalability solutions.
This development makes Glacier Drop the largest application currently operating on the Cardano mainnet, marking a decisive step toward the mass adoption of its decentralized infrastructure.
Midnight implemented this strategy to prevent hundreds of thousands of claims from directly impacting the main network. Instead, each Hydra Head receives the requests, validates them, consolidates the results, and subsequently publishes summarized executions on the Cardano blockchain. This approach reduces latency, minimizes costs, and maintains peak performance even under heavy load.
The operators who keep Hydra Heads active
For Glacier Drop, each Hydra Head is operated by a set of independent infrastructure operators. Together, these operators run a Head that validates claims, reach consensus on their validity, and post the final outcomes (NIGHT redemption contracts) to the Cardano blockchain. Before any transaction is recorded on the blockchain, all nodes must reach consensus, ensuring decentralization and security.
The selection of these ecosystem partners is strategic, with each organization contributing distinct and complementary capabilities.
- Alchemy, a leading blockchain development platform, brings its focus on providing developers with foundational tools and infrastructure. Its role as a partner validates the Hydra deployment as a stable and robust foundation upon which future developers can build decentralized applications.
- Anastasia Labs is a blockchain software consultancy that provides enterprise-grade engineering and reliability. Its participation helps diversify the operator base beyond incumbent organizations, showing that Hydra can be adopted and run effectively by independent technical specialists.
- BitGo, an institutional qualified custodian, operates one of the nodes and its participation provides a high degree of security and assurance. This dual role demonstrates that the Hydra protocol meets the stringent standards required for institutional-grade applications.
- Blockdaemon secures $110B+ in digital assets and provides institutional-grade blockchain infrastructure for world-leading financial institutions. It will contribute its extensive experience in operating secure and scalable nodes to ensure Hydra deployment is managed with a high degree of operational security and reliability.
- Input Output Engineering (IOE), the original architect of the protocol, ensures the deployment aligns with Hydra’s core design and research principles. Their direct involvement bridges the gap between academic theory and production-grade implementation, validating that the technology functions as intended at a critical moment of ecosystem adoption.
- SundaeLabs brings extensive expertise from across the ecosystem including open-source Hydra contributions and the world’s first Hydra smart contract demo. Their involvement ensures the Hydra implementation is aligned with the demands of transaction-heavy use cases.
A collaborative model for scalable infrastructure
Together, the partners create a balanced and resilient operator set for processing claims at scale during Glacier Drop.
The direct implications of this model extend to every part of the ecosystem. For community participants, the result is a faster, cheaper, and more reliable claim process. For developers, it offers a practical demonstration that Hydra can be integrated into production applications, moving it from an academic concept to a production-grade L2. Furthermore, for institutions, the active involvement of these ecosystem partners provides crucial validation that Hydra’s architecture is secure enough for high-value operations.
Ultimately, Glacier Drop functions as a large-scale, real-world use of Hydra’s capacity to handle high transaction volumes and validating its readiness for complex applications. It establishes a functional precedent for how high-throughput use cases, from decentralized finance to institutional services, can operate at scale, with the Midnight network serving as a customer and catalyst for this next generation of infrastructure.
Do you know what staking is ? Staking on the blockchain refers to the process where participants lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency to support the operations and security of a blockchain network. In return, they earn rewards, typically in the form of additional cryptocurrency. Staking is often associated with proof-of-stake (PoS) or similar consensus mechanisms used by many blockchains.
Partners :
